Validation Exchange Theory describes how leaders strengthen engagement by verifying the accuracy of a worker’s deliverables and providing authentic validation in return. This manuscript formalizes the theory through a mechanistic equation and evaluates its behavior through controlled stress testing. Two independent AI architectures validated the model’s accuracy under multiple conditions, confirming the predictive structure of the theory...

Last Updated: 2025-12-17 14:51 UTC Reasoned Leadership (2.0) is a mechanistic leadership framework designed to model, evaluate, and develop leadership capability under conditions of uncertainty, complexity, and adversity. It is grounded in cognitive science, behavioral mechanisms, systems reasoning, and strategic execution, and provides a structured approach to accurate decision-making, bias disruption, and leadership development. For a basic...

The 3B Behavior Modification Model maps the progression from emotion to bias, bias to belief, and belief to behavior. This manuscript presents a formal, mechanistic framework that illustrates how emotional triggers influence cognitive filters and ultimately shape behavioral outputs. Simulation confirms the model’s predictive reliability across stress and stability conditions. The model serves as a core behavioral engine within the Reasoned...

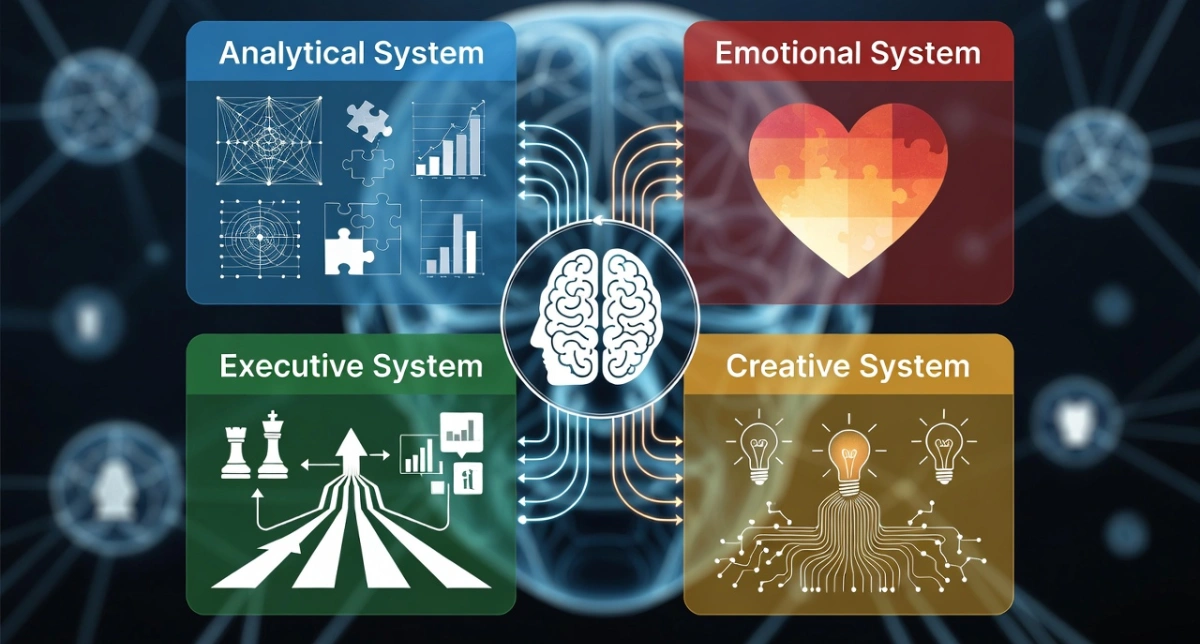
The Multi-Modal Reflection Protocol (MMRP) is a Reasoned Leadership critical reflection framework designed to force systematic engagement across four distinct neural processing systems during learning. Unlike conventional reflection practices that aim for deep encoding, MMRP engineers it through structured interrogation that targets analytical, emotional, executive, and creative faculties. The result is redundant storage pathways, integrated...

Part 1 - Organizational Needs There is a considerable amount of literature dedicated to organizational perspectives of leadership and organizational development. The bulk of published works tends to focus on the topic from the lens of various industries, individual organizations, or existing leadership within the organization. While these studies provide valuable insight into development and its potential barriers, they may not have examined...

Part 2 - The Reality of Leadership Development For organizations in the know, professional leadership development in both the public and private sectors has become a very popular endeavor (Edwards et al., 2015). Leadership development is often considered a strategic necessity for organizations that want to thrive in the rapidly changing and competitive business environment (Dalakoura, 2010). However, despite the need for strong leadership in...

Part 3 - Leadership Development Evaluations And Limitations There are a lot of question marks regarding development measurement. Perhaps there is a mismatch between the actual outcome of development and organizational expectations, or perhaps the knowledge of appropriate measurement is not well-known yet. Either way, there is a clear divide between what science knows and what is expected by many organizational leaders regarding development...

Part 4 – Hiring the Right Trainer – The Novice Factor The inability to effectively measure newer development models presents a strong and legitimate question of how an individual or organization can trust leadership and organizational development efforts and investments. Gaining the necessary trust requires a better understanding of the leadership industry and selecting the right professionals and development services. However, this task is...

Part 5 – Fundamental Confusion: Management Vs. Leadership Unfortunately, there are no universally accepted definitions for either leadership or management. Hundreds of definitions exist for both. However, leadership can be defined as a process of social influence that maximizes others' efforts toward achieving a goal (Kruse, 2013) or a series of complex interactions between the leader and stakeholders in the organizational environment...

Part 6 – Organizational Culture In this final installment, the discussion turns to organizational culture and toxicity. The issue is often circular because one problem feeds the next, which feeds the first. Similarly, the correction is found at both the beginning and the end. What follows is merely a demonstration of this circle, some of the overlap, the seemingly inevitable consequence, and a potential solution. In almost any setting,...